Edge computing and Content Delivery Networks (CDN) are two important technologies in the digital world. They both aim to improve data delivery but work differently.
Understanding the difference between them can help businesses make better decisions. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency. It is ideal for real-time applications and IoT devices. CDNs, on the other hand, focus on delivering web content faster by caching it in various locations worldwide.
This speeds up access for users across different regions. Comparing these technologies helps businesses choose the right solution for their needs. Edge computing offers immediacy, while CDNs provide global reach. Knowing how each operates can guide you in optimizing performance and improving user experiences. Let's explore their differences to make informed choices for your digital strategy.
Credit: www.akamai.com
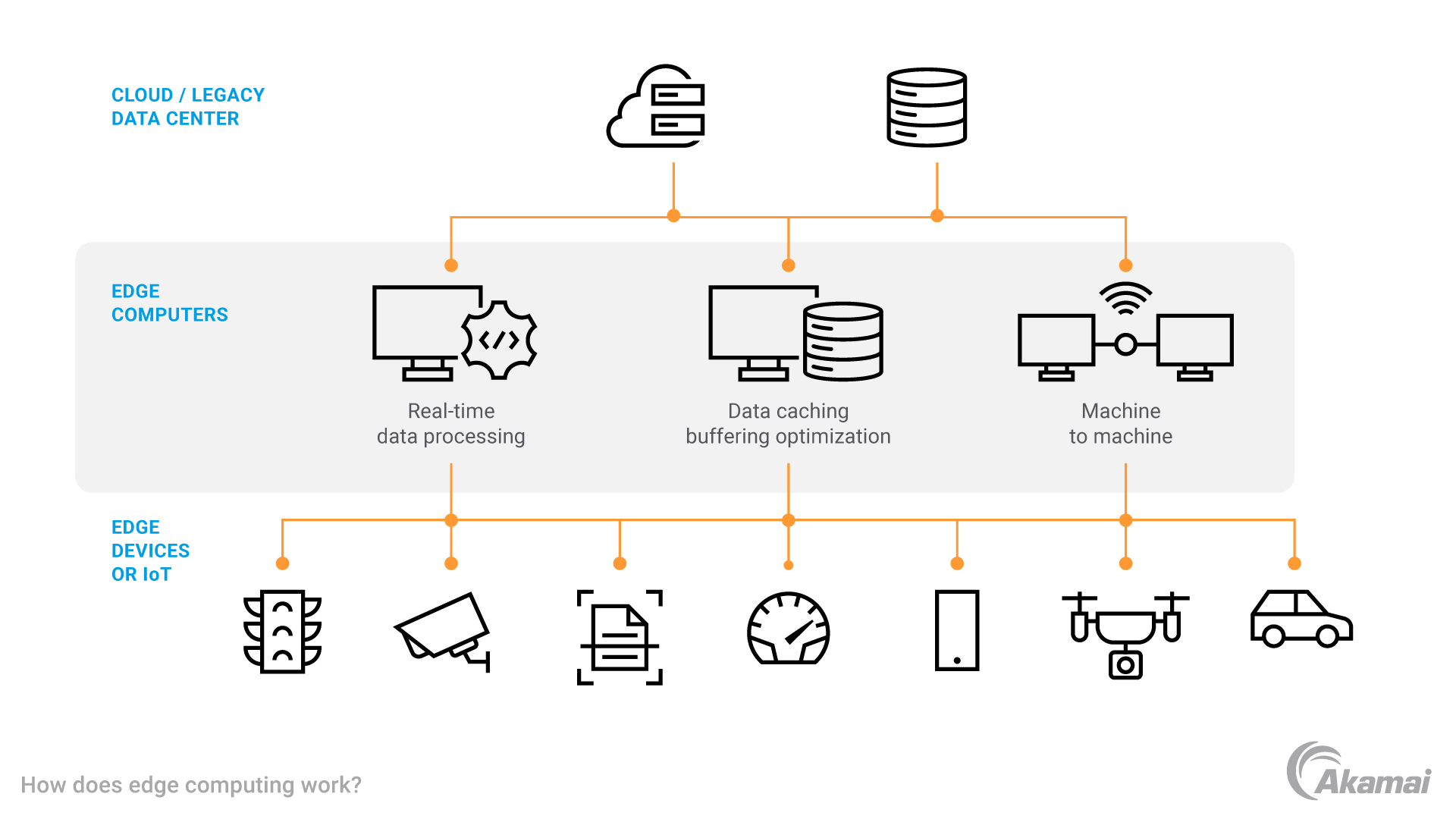
Introduction To Edge Computing
Understanding edge computing starts with grasping its core concept. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency. This approach contrasts with traditional cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers. Edge computing's proximity to the data source offers faster processing and real-time analysis. It proves essential for applications needing quick response times.
Emergence Of Edge Technology
Edge technology emerged from the need for faster data handling. As devices grew smarter, the demand for quick data processing increased. IoT devices require immediate data insights. Edge computing addresses this by processing data at the network's edge. This reduces data travel time and enhances performance.
Benefits Of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several advantages. It minimizes latency, ensuring prompt data responses. This is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles. Edge computing enhances data privacy. Data remains close to its source, reducing exposure risks. It also lowers bandwidth costs by processing data locally. This efficient approach saves resources and improves overall system performance.
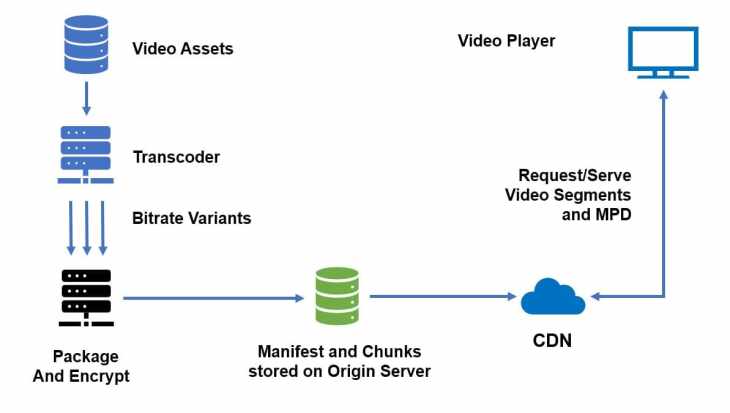
Overview Of Cdn
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in modern web infrastructure. They ensure fast delivery of internet content globally. By distributing services geographically, CDNs enhance user experience and reduce latency.
Purpose Of Content Delivery Networks
CDNs improve content accessibility. They store copies of content across multiple locations. This means users can access data from a nearby server. It reduces load times significantly. Faster load times lead to a better user experience. This can also improve search engine rankings. Businesses benefit from increased engagement and reduced bounce rates.
How Cdns Operate
CDNs operate through a network of servers. These servers cache content close to users. When a user requests content, the CDN delivers it from the nearest server. This minimizes the distance data travels. It results in faster load times. CDNs also handle large volumes of traffic. They prevent website crashes during high demand periods.
CDNs use advanced technologies for efficient data delivery. Load balancing and real-time analytics are common features. These technologies ensure optimal performance. They help in distributing traffic evenly. This maintains website reliability and speed.
Core Differences
Understanding the core differences between edge computing and CDN is crucial. Each plays a unique role in data management and delivery. They both aim to enhance user experience but operate differently. Let's delve into what sets them apart.
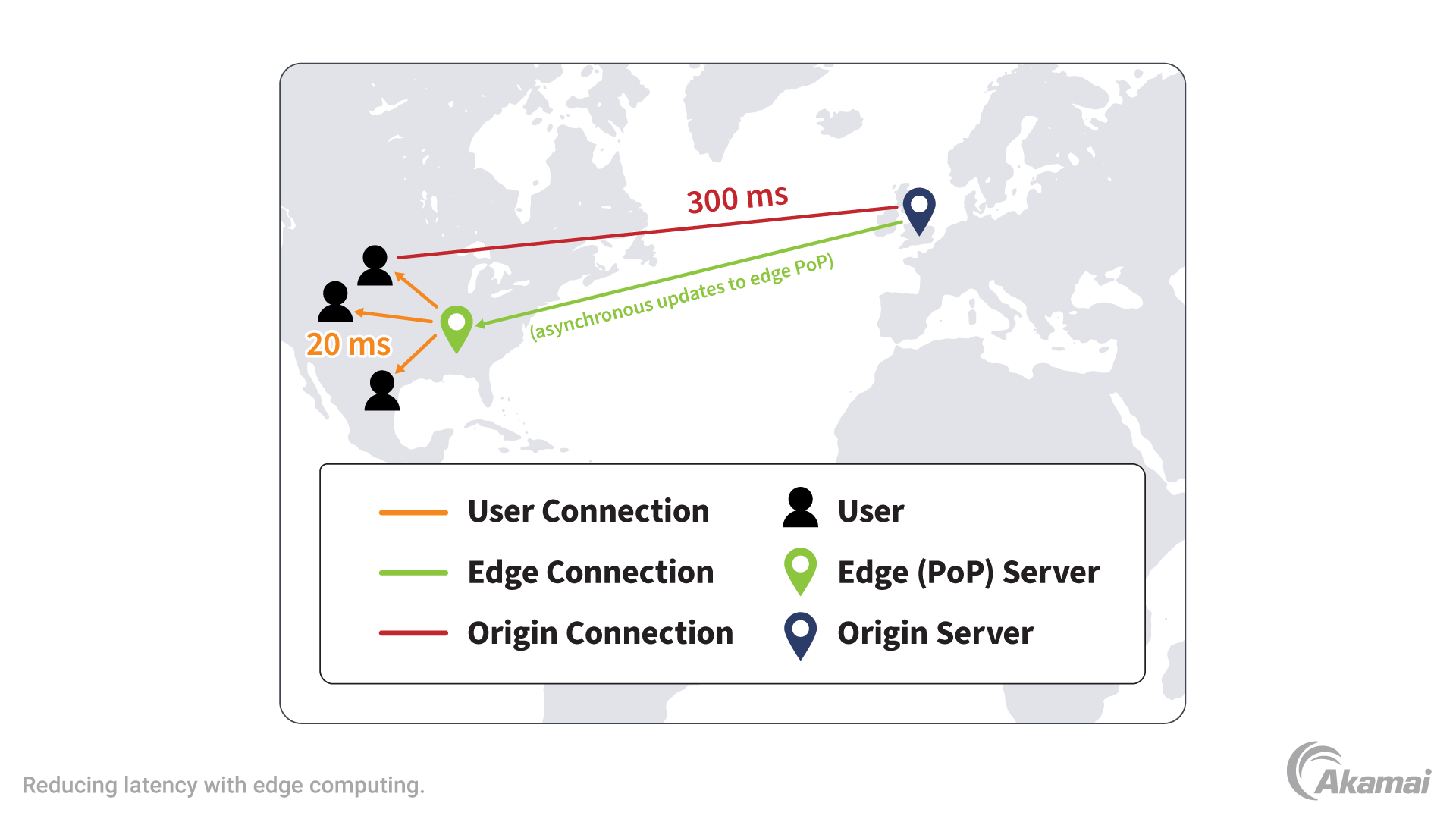
Data Processing Location
Edge computing processes data near the source, close to users. This happens at the network's edge. It reduces the need to send data to centralized servers. In contrast, CDN stores and delivers content from various locations. These are spread across the globe. It caches data closer to users but processes it centrally.
Latency And Performance
Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data locally. Users experience faster response times and improved performance. This is vital for real-time applications. CDN reduces latency by caching content near users. It speeds up loading times for static content like images and videos. Both enhance performance but in different ways.
Credit: bunny.net
Use Cases For Edge Computing
Edge computing is transforming how data gets processed and managed. It brings computation closer to data sources, enhancing speed and efficiency. This method is vital for applications needing quick responses. Let's explore some use cases where edge computing excels.
Iot Applications
Edge computing plays a crucial role in IoT applications. Devices like smart thermostats and home assistants rely on it. They process data locally, ensuring fast response times. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage. It allows devices to function even without internet connectivity. Edge computing enhances security by limiting data exposure. Sensitive information remains on the device, minimizing risks.
Real-time Data Processing
Real-time data processing is essential in many industries. Edge computing provides the necessary speed for quick decision-making. For example, self-driving cars use edge computing for instant data analysis. They process sensor data on the spot, ensuring safe navigation. In healthcare, wearable devices monitor vital signs in real-time. Edge computing ensures timely alerts for medical professionals. This swift data processing improves efficiency across sectors.
Cdn Use Cases
Content Delivery Networks, or CDNs, play a crucial role in modern web experiences. They enhance speed, reliability, and performance. Understanding their use cases helps in leveraging their full potential. Let's explore two primary applications of CDNs.
Website Optimization
CDNs significantly boost website loading times. They store copies of your site on servers worldwide. Users access the server closest to them. This reduces latency and enhances user experience. Fast websites keep visitors engaged longer. They also help in reducing bounce rates. CDNs provide automatic load balancing. This ensures websites stay online during traffic spikes.
Streaming Media
Streaming media benefits greatly from CDNs. They deliver videos smoothly, without buffering. This ensures a consistent viewing experience. CDNs distribute video content globally. Viewers get content from the nearest server. This reduces load times and buffering. High-quality streaming becomes possible with CDNs. They support various media formats seamlessly. This makes them ideal for live events and on-demand videos.
Credit: www.akamai.com
Scalability And Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are crucial in today's digital landscape. They ensure systems handle growth and adapt to changes. Edge computing and CDN offer unique benefits in these areas. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right solution.
Edge Computing Scalability
Edge computing scales by distributing processing power. It places resources closer to the data source. This method reduces latency and improves performance. As demand grows, more edge nodes can be added. This approach supports real-time data processing. It benefits applications needing immediate responses. Think IoT devices and smart cities. Edge computing ensures efficient resource management. It adapts to varying workloads with ease.
Cdn Flexibility
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) offer great flexibility. They optimize content delivery across various regions. CDNs cache content at multiple locations globally. This reduces load times for users worldwide. They adapt to network conditions and traffic patterns. CDNs also manage sudden traffic spikes effectively. They distribute traffic across numerous servers. This balances load and maintains performance. CDNs support different content types, from images to videos. They ensure consistent user experiences.
Security Implications
When you think about data management and delivery, security is a top concern. Edge computing and CDN (Content Delivery Network) each offer unique security implications. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions about which technology best suits your needs. Both have their strengths and challenges. Let's dive into these aspects to see how they might affect your digital strategy.
Edge Security Challenges
Edge computing decentralizes data processing, bringing it closer to the user. This proximity can lead to security vulnerabilities if not managed properly. The distributed nature of edge devices means a larger attack surface. This can increase the risk of unauthorized access.
Imagine devices scattered across various locations, each potentially exposed to different security threats. How do you ensure that every device maintains the same level of security? It's a question worth pondering. Implementing robust authentication and encryption protocols is crucial.
Real-time data processing at the edge also presents challenges. You need to ensure that data integrity is maintained during rapid exchanges. It's like juggling multiple balls in the air; one slip can lead to compromise.
Cdn Security Measures
CDNs are more centralized than edge computing. This centralization can simplify security management. With a CDN, you have fewer nodes to secure, which can reduce potential vulnerabilities.
CDNs often come equipped with built-in security features. These can include DDoS protection, secure sockets layer (SSL) encryption, and firewalls. These measures help protect against common attacks, keeping your data safe during delivery.
However, reliance on a central point can also be a single point of failure. What happens if the CDN provider faces a security breach? It's vital to have contingency plans and regular security audits to minimize risks.
Ultimately, the choice between edge computing and CDN should factor in your specific security needs. Which challenges are you prepared to tackle? Do you prioritize speed over security, or vice versa? Your answers will guide you to the right solution.
Future Trends
Technology is evolving rapidly. Edge computing and CDN (Content Delivery Network) are adapting to meet future demands. Understanding upcoming trends helps businesses plan effectively. It also improves efficiency and performance.
Advancements In Edge Computing
Edge computing is getting smarter. Devices process data closer to the source. This reduces latency and speeds up tasks. More industries are using edge computing. It's becoming crucial for real-time applications.
AI integration is a major trend in edge computing. AI algorithms run at the edge. This allows faster decision-making. Edge computing networks are growing. More devices are connecting every day. This is transforming IoT ecosystems.
Evolving Cdn Technologies
CDNs are expanding their capabilities. They deliver content faster and more reliably. Improved caching techniques enhance performance. Dynamic content delivery is a focus area. It ensures users get updated information quickly.
Security is a priority for CDNs. New protocols protect against cyber threats. Scalable architectures handle increasing traffic. This ensures smooth user experiences. CDNs are crucial for handling large-scale digital content.
Combining CDN and edge computing is a trend. It offers better content distribution. Users enjoy faster, safer access. This synergy is shaping the future of digital experiences.
Choosing The Right Solution
Choosing the right solution between Edge Computing and CDN is crucial. Both have unique benefits. Each serves different business needs. Understanding these differences helps make informed decisions.
Evaluating Business Needs
Begin by assessing your business requirements. Consider the nature of your data. Do you need real-time processing? Edge Computing may suit you. For content delivery, CDN might be better. Reflect on your business scale. Larger operations may need both. Smaller businesses might find one sufficient.
Integration Considerations
Think about integration with existing systems. Edge Computing might require new infrastructure. This could increase costs. CDN integrates more easily. It often uses existing internet networks. Evaluate your technical team's skills. Ensure they can manage the chosen solution. Training might be necessary for Edge Computing. CDN might need less technical expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Cdn And Edge Computing?
CDN delivers content from the nearest server to reduce latency. Edge computing processes data closer to the data source, enhancing speed and efficiency. Both improve performance but serve different purposes in data management and delivery.
What Role Do Edge Locations Play In The Cdn?
Edge locations store cached content close to users, reducing latency and improving load times. They enhance user experience by delivering data quickly. These locations are vital in optimizing website speed and performance, ensuring efficient content delivery across global networks.
What Is The Difference Between Edge Computing And Cloud Computing?
Edge computing processes data near its source, reducing latency. Cloud computing handles data remotely in centralized data centers. Edge computing enhances real-time processing, while cloud computing offers scalability and storage. Both complement each other for efficient data management.
What Is The Difference Between Internet Of Things And Edge Computing?
The Internet of Things connects devices to the internet, facilitating data exchange. Edge computing processes data locally, near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use. IoT and edge computing complement each other, enhancing efficiency and real-time data processing in smart devices and systems.
Conclusion
Edge computing and CDN both enhance online experiences. They serve different purposes. Edge computing processes data near the source. It reduces latency and improves speed. CDN distributes content across multiple servers. This ensures efficient delivery and reduces load times. Choosing the right option depends on your needs.
Edge is ideal for real-time data processing. CDN is perfect for content distribution. Both technologies play crucial roles today. Understanding their differences helps in making informed decisions. Optimize your strategy for the best results. Focus on user experience and performance.
This boosts engagement and satisfaction.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the difference between CDN and edge computing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “CDN delivers content from the nearest server to reduce latency. Edge computing processes data closer to the data source, enhancing speed and efficiency. Both improve performance but serve different purposes in data management and delivery.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What role do edge locations play in the CDN?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge locations store cached content close to users, reducing latency and improving load times. They enhance user experience by delivering data quickly. These locations are vital in optimizing website speed and performance, ensuring efficient content delivery across global networks.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the difference between edge computing and cloud computing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge computing processes data near its source, reducing latency. Cloud computing handles data remotely in centralized data centers. Edge computing enhances real-time processing, while cloud computing offers scalability and storage. Both complement each other for efficient data management.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the difference between Internet of Things and edge computing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The Internet of Things connects devices to the internet, facilitating data exchange. Edge computing processes data locally, near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use. IoT and edge computing complement each other, enhancing efficiency and real-time data processing in smart devices and systems.” } } ] }