Edge computing is transforming how we process data. It brings computation closer to data sources.
This reduces latency and boosts efficiency. In today's digital age, the demand for fast data processing is skyrocketing. Traditional cloud computing can't always keep up. This is where edge computing shines. By processing data near its source, it reduces delays and improves response times.
Industries worldwide are tapping into this tech marvel. From smart cities to autonomous vehicles, edge computing is making a mark. It supports real-time decision-making and enhances user experiences. As more devices connect to the internet, its role will only grow. Understanding where edge computing is applied can offer insights into its potential. Let's explore the diverse application areas of edge computing.
Introduction To Edge Computing
Edge computing is transforming how data is processed and analyzed. This technology brings computing closer to the source of data. It reduces latency and improves speed. Traditional cloud computing relies on centralized data centers. Edge computing decentralizes data processing. This shift is crucial for real-time applications.
Edge computing supports industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. It enhances efficiency and reduces costs. Understanding its principles can help businesses thrive. Let's explore the history and core principles of edge computing.
Brief History
The concept of edge computing emerged in the early 2000s. It evolved from the need for faster data processing. As devices became smarter, data processing demands increased. Early implementations focused on reducing latency. This was essential for applications requiring real-time data.
Over time, technology advancements fueled edge computing growth. The rise of IoT devices played a major role. These devices generate vast amounts of data. Processing this data at the edge improved performance. Today, edge computing is integral to digital transformation strategies.
Core Principles
Edge computing revolves around decentralizing data processing. It brings computation close to data sources. This reduces the need for long-distance data transmission. Local data processing decreases network congestion. It enhances response times for critical applications.
Scalability is another core principle of edge computing. It allows for efficient resource management. Edge computing adapts to varying data loads. This flexibility is vital for dynamic environments. Security is also a key focus. Processing data locally minimizes exposure to threats.
These principles make edge computing a powerful tool. Businesses can leverage it for improved performance. It supports innovation in data-intensive industries. Understanding these principles is crucial for successful implementation.
Industry Impact
Edge computing is reshaping industries by bringing data processing closer to the source. This proximity allows for quicker data analysis, reduced latency, and improved efficiency. By examining its impact on healthcare and manufacturing, you can discover how edge computing is transforming these sectors.
Healthcare Advances
Imagine being able to monitor a patient's vital signs in real-time, no matter where they are. Edge computing makes this possible by processing data at the source, reducing the need for centralized data centers.
Devices like wearable health monitors can provide immediate insights to healthcare professionals. This means faster response times in emergencies and tailored treatment plans. What could this mean for patient outcomes?
Consider the potential for remote surgeries powered by edge computing. Surgeons can perform procedures with precision, guided by real-time data. This isn't just a vision of the future; it's happening now, changing the landscape of healthcare.
Manufacturing Evolution
In manufacturing, edge computing is enhancing productivity and efficiency. Imagine a factory where machines can predict maintenance needs before a breakdown occurs. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and saves costs.
Edge computing enables real-time monitoring of machinery, allowing for immediate adjustments. This means higher quality products and faster production cycles. How much could your business save with such advancements?
Picture smart factories utilizing edge computing to automate processes. This technology is not just about efficiency; it's about creating safer work environments and optimizing resource use. The evolution is happening, and it's transforming manufacturing practices.
Smart Cities Development
Smart cities rely on cutting-edge technology to improve urban life. Edge computing plays a crucial role here. It processes data closer to the source. This reduces latency and enhances efficiency. Smart cities can respond faster to real-world situations.
Edge computing helps manage resources better. It supports sustainable and smart urban growth. Let's explore two key areas: traffic management and public safety.
Real-time Traffic Management
Edge computing makes real-time traffic management possible. Sensors gather data from roads and vehicles. This data is processed locally, not sent to distant servers. The result? Faster decisions and smoother traffic flow.
Traffic signals adjust dynamically. They respond to real-time conditions. This reduces congestion and travel time. It also improves fuel efficiency and lowers emissions. Commuters enjoy less stress and more reliable travel times.
Public Safety Enhancement
Public safety is a top priority in smart cities. Edge computing enhances this by processing data swiftly. Surveillance cameras and sensors monitor urban areas. Edge devices analyze the data on-site.
Quick analysis detects unusual activities. This allows faster response to emergencies. It improves safety for residents and visitors. Advanced systems can even predict potential threats. This proactive approach helps prevent incidents.

Credit: www.apriorit.com
Retail And Consumer Experiences
Edge computing is transforming the retail landscape. It enhances consumer experiences by processing data close to the source. This technology brings speed and efficiency, offering retailers a competitive edge. By analyzing data in real-time, retailers can meet customer demands more precisely. Let's explore how edge computing impacts retail through personalized shopping and inventory optimization.
Personalized Shopping
Edge computing empowers personalized shopping by analyzing customer data instantly. Retailers can provide tailored recommendations at the right moment. This enhances customer satisfaction and boosts sales. By processing data at the edge, stores can adapt to customer needs quickly. It creates a seamless and personalized shopping experience for each visitor.
Inventory Optimization
Efficient inventory management is crucial for retail success. Edge computing helps optimize inventory by providing real-time data insights. This technology ensures shelves are stocked with the right products. Retailers reduce waste and improve stock availability. By predicting demand accurately, stores can minimize overstock and stockouts. Edge computing thus enhances operational efficiency in retail.
Agriculture And Farming
Agriculture and farming are evolving with technology. Edge computing plays a key role. It helps farmers make smarter decisions. This technology brings computing power closer to where data is generated. Edge computing reduces latency and increases efficiency. It is transforming traditional farming methods. It enhances productivity and sustainability.
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses edge computing to gather real-time data. Farmers use sensors placed in fields. These sensors collect data about soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. Edge computing processes this data instantly. It helps farmers make quick decisions. They can optimize water usage and apply fertilizers accurately. This reduces waste and improves crop yield.
Farm Automation
Farm automation relies heavily on edge computing. Machines like drones and tractors use edge computing. They perform tasks without human intervention. Drones survey fields and collect images. Edge computing analyzes these images for pest detection. Automated tractors plant and harvest crops efficiently. This reduces labor costs and increases productivity. Edge computing makes farm operations smoother and faster.
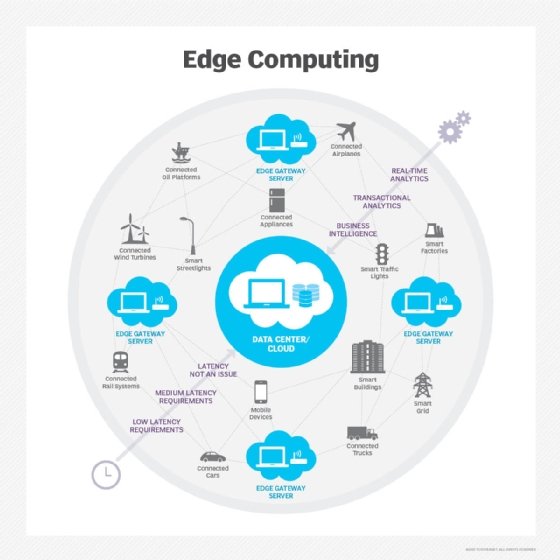
Credit: www.techtarget.com
Energy And Utilities
Edge computing enhances energy and utilities by improving data processing speed. It enables real-time monitoring of energy consumption. This technology also supports efficient grid management and reduces operational costs.
In the world of energy and utilities, edge computing is transforming how we manage and distribute power. This technology brings computing power closer to the source of data, enabling faster processing and more efficient operations. As our demand for energy grows, edge computing offers innovative solutions to optimize and enhance the way we consume and generate power.Grid Management
Effective grid management is crucial for reliable energy delivery. Edge computing helps by processing data from sensors and devices installed throughout the power grid. This enables real-time monitoring and quick responses to fluctuations or faults. Imagine a power outage in your neighborhood. With edge computing, utility companies can quickly identify the problem's location and address it faster than ever before. The system can analyze data on-site, reducing the time it takes to restore power and improving overall grid reliability. Edge computing also enhances predictive maintenance. By analyzing data locally, it can forecast potential equipment failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring a more stable power supply for everyone.Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources into the grid is a complex task. Edge computing simplifies this by managing the flow of energy from wind, solar, and other renewable sources. It ensures a smooth and balanced energy supply even when these sources are intermittent. Consider solar panels on your rooftop. Edge computing can manage the electricity they generate, deciding when to store, use, or feed it back into the grid. This local decision-making optimizes energy use and reduces waste, benefiting both you and the environment. It also supports microgrids, which are localized energy systems that can operate independently. With edge computing, microgrids can efficiently manage energy distribution, making them ideal for remote or rural areas. This helps bring renewable energy to communities that might otherwise lack access to reliable power sources. Edge computing in energy and utilities isn't just about technology; it's about making our power systems smarter and more resilient. How will you embrace this change in your energy consumption?Transportation And Logistics
Edge computing is transforming transportation and logistics. It offers real-time data processing at the source. This reduces delays and enhances decision-making. With edge computing, businesses can optimize operations. They can reduce costs and improve efficiency. It is a key technology in modern logistics.
Fleet Tracking
Edge computing enhances fleet tracking. It processes data directly from vehicles. This helps monitor location and speed instantly. Managers receive updates faster. It improves route planning and reduces fuel consumption. Real-time tracking is a game-changer for fleet management.
Supply Chain Efficiency
Edge computing boosts supply chain efficiency. It processes data at each step of the chain. This helps identify bottlenecks quickly. Businesses can respond to disruptions faster. It ensures goods reach their destination on time. Improved efficiency means happier customers.
Challenges And Future Prospects
Edge computing is transforming various industries with its innovative approach. Yet, it comes with its own set of challenges and future prospects. These hurdles are pivotal in shaping its adoption and effectiveness. As the technology advances, addressing these issues becomes crucial.
Security Concerns
Security remains a major challenge in edge computing. Data processed locally can be vulnerable to breaches. Devices often lack robust security measures. This exposes sensitive information to risks. Keeping data secure requires constant vigilance. Advanced encryption and authentication can help mitigate threats. Regular updates are also essential to safeguard devices.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is another significant hurdle. Edge computing involves numerous devices in varied locations. Managing a growing number of devices can be complex. Infrastructure must adapt to increased demand efficiently. Ensuring consistent performance across devices is vital. Solutions like automation can ease scalability challenges. Scalable architecture design is also crucial for future growth.
Addressing these challenges will determine edge computing's future success. With the right strategies, the technology can continue to evolve. It holds the potential to enhance many applications. By overcoming hurdles, edge computing can achieve broader adoption and impact.

Credit: insights.daffodilsw.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Application Areas Of Edge Computing?
Edge computing is used in IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, healthcare, and industrial automation. It enables real-time data processing, reduces latency, and enhances data security. Edge computing supports applications like video streaming, augmented reality, and remote monitoring. It optimizes bandwidth and improves system efficiency in distributed networks.
What Are The Application Areas Of Edge Detection?
Edge detection is crucial in image processing, computer vision, and robotics. It assists in object detection, facial recognition, and medical imaging. It enhances video surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and industrial inspection. Edge detection improves image segmentation and feature extraction in various applications.
What Are Some Examples Of Edge Computing?
Edge computing examples include smart home devices, autonomous vehicles, and wearable health trackers. These technologies process data locally, enhancing speed and efficiency. Industrial IoT sensors and retail analytics systems also utilize edge computing for real-time insights and improved decision-making. Edge computing minimizes latency by bringing computation closer to the data source.
What Are The Applications Of Edge Ai?
Edge AI applications include real-time data processing in IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart home systems. It enhances security with instant facial recognition and supports healthcare through wearable monitoring. Edge AI also optimizes industrial automation, enabling predictive maintenance and efficient resource management.
Conclusion
Edge computing is changing the digital landscape. It brings data processing closer to devices. This reduces latency and improves speed. Many industries benefit from edge computing. Healthcare sees quicker data access. Manufacturing gets real-time monitoring. Retail enhances customer experiences. Edge computing boosts efficiency across sectors.
Its potential is vast and growing. Businesses can adapt to edge solutions. They can improve operations and services. Edge computing is a step toward a smarter future. As technology evolves, edge computing will expand. Understanding its role helps in adapting to innovations.
Stay informed, and embrace its possibilities.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the application areas of edge computing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge computing is used in IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, healthcare, and industrial automation. It enables real-time data processing, reduces latency, and enhances data security. Edge computing supports applications like video streaming, augmented reality, and remote monitoring. It optimizes bandwidth and improves system efficiency in distributed networks.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the application areas of edge detection?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge detection is crucial in image processing, computer vision, and robotics. It assists in object detection, facial recognition, and medical imaging. It enhances video surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and industrial inspection. Edge detection improves image segmentation and feature extraction in various applications.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are some examples of edge computing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge computing examples include smart home devices, autonomous vehicles, and wearable health trackers. These technologies process data locally, enhancing speed and efficiency. Industrial IoT sensors and retail analytics systems also utilize edge computing for real-time insights and improved decision-making. Edge computing minimizes latency by bringing computation closer to the data source.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the applications of edge AI?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Edge AI applications include real-time data processing in IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart home systems. It enhances security with instant facial recognition and supports healthcare through wearable monitoring. Edge AI also optimizes industrial automation, enabling predictive maintenance and efficient resource management.” } } ] }